Healthcare revenue cycle management (RCM) is the financial process that tracks patient care from the moment of initial contact through to final payment collection. In hospital settings, this process is more complex due to the higher patient volume, diverse services, and strict regulatory requirements. A well-structured RCM system ensures that hospitals are reimbursed accurately and on time for the care they provide.
In simple terms, RCM is the backbone of a healthcare organization’s financial health. It connects the clinical side of patient care with the administrative and financial functions, turning medical services into revenue. This process includes verifying patient insurance, coding diagnoses and procedures, submitting claims, following up on unpaid claims, and processing patient payments.
Why RCM is Mission Critical for Financial Performance
For hospitals and healthcare systems, efficient RCM is essential to maintaining cash flow, funding operations, and reinvesting in patient care. Without it, errors, delays, and denied claims can lead to significant revenue loss. An optimized revenue cycle reduces days in accounts receivable (A/R), minimizes billing errors, and improves compliance with payer and regulatory requirements.
In an era where healthcare margins are increasingly tight, strong revenue cycle management also supports better patient satisfaction. Clear communication about costs, faster billing processes, and accessible payment options all contribute to a more positive patient experience.
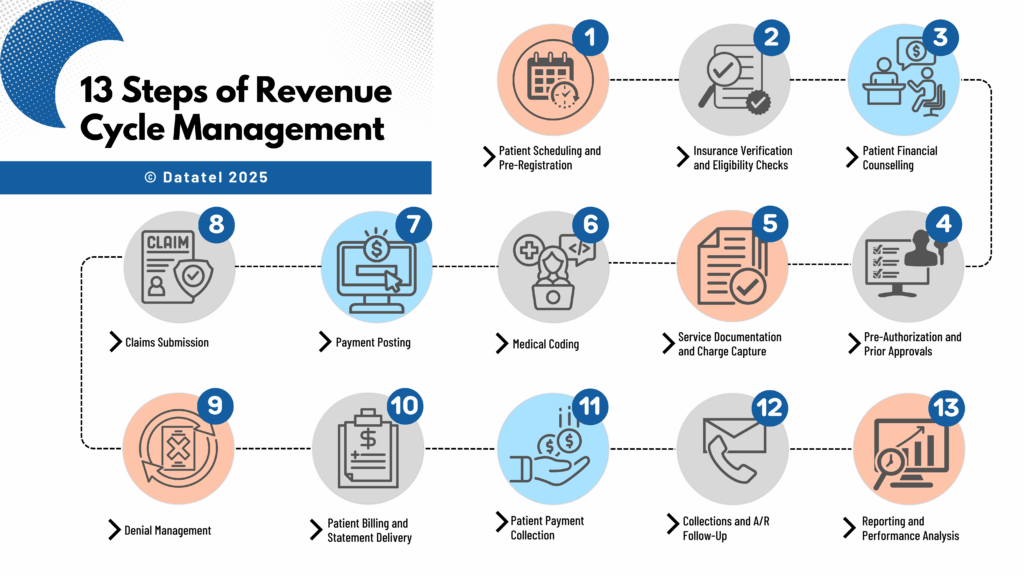
13 Steps of Revenue Cycle Management in Healthcare
The 13 steps of revenue cycle management in healthcare outline the complete journey from the moment a patient schedules care to the final payment posting. Each step plays a vital role in ensuring hospitals and healthcare providers maintain healthy cash flow, reduce costly delays, and protect compliance. When one step is overlooked or poorly managed, it can create a ripple effect that impacts the entire cycle.
Step 1 – Patient Scheduling and Pre-Registration
The hospital revenue cycle begins when a patient books an appointment or procedure. This step sets the foundation for accurate billing and efficient processing. Collecting complete demographic and insurance information at the time of scheduling allows hospitals to prepare in advance. Pre-registration also ensures patients are informed about documentation requirements and potential out-of-pocket costs, reducing surprises later in the process. A strong pre-registration workflow can cut registration time at check-in by up to 50 percent and lower claim denial rates.
Step 2 – Insurance Verification and Eligibility Checks
Insurance verification in healthcare revenue cycle management confirms a patient’s coverage, benefit limits, and pre-authorization requirements. Automating eligibility checks through integrated RCM tools helps staff identify discrepancies before care is provided. For example, a real-time eligibility tool can instantly confirm whether a service is covered and what portion the patient will owe, preventing delays caused by incomplete or inaccurate details.
Step 3 – Patient Financial Counselling
Discussing costs upfront is critical for patient trust and payment compliance. Patient financial counselling can include providing written cost estimates, outlining available payment plans, and explaining financial assistance programs. Hospitals that invest in this step often see reduced A/R days because patients are prepared for their financial responsibility and more likely to pay on time. This step also improves patient satisfaction by eliminating the confusion that can lead to billing disputes.
Step 4 – Pre-Authorization and Prior Approvals
Certain services, procedures, or medications require payer pre-authorization before treatment. Pre-authorization in hospital RCM involves submitting medical necessity documentation and awaiting payer approval. Failure to complete this step accurately can lead to claim denials that are difficult to overturn. Hospitals benefit from having a dedicated pre-authorization team or automated workflows that track requests and flag any missing information before the scheduled date of service.
Step 5 – Service Documentation and Charge Capture
Every service provided must be documented to be billable. Charge capture ensures that no services or supplies go unbilled, which can significantly impact revenue. Missing charges are often the result of incomplete documentation, poor communication between clinical and billing teams, or manual errors. Implementing electronic health record (EHR) templates and automatic charge capture tools helps reduce revenue leakage and ensures billing accuracy.

Step 6 – Medical Coding
Medical coding translates documented care into standardized codes, such as ICD-10, CPT, and HCPCS, which are required for claim submission. Accurate coding is critical for compliance and correct reimbursement rates. Hospitals with robust coding audit programs reduce the risk of payer audits, underpayments, or overpayments that may later require refunds. Ongoing coder education is essential to stay ahead of annual updates and regulatory changes.
Step 7 – Claims Submission
The claims submission step in RCM is where all collected data (patient information, coding, and charges) is compiled and sent to payers. Clean claims that meet payer requirements the first time are processed faster and reduce rework. Submitting claims electronically through a clearinghouse increases efficiency and allows for quick error detection before claims reach the payer.
Step 8 – Payment Posting
After the payer processes a claim, payment posting in the healthcare revenue cycle involves applying the payment to the patient’s account and reconciling it against the billed amount. This step ensures accurate financial reporting and allows staff to quickly identify any underpayments or overpayments. Automated payment posting systems speed up reconciliation and free staff to focus on exceptions and problem accounts.
Step 9 – Denial Management
Even with clean claims, denials in hospital revenue cycle management are inevitable. Denial management teams investigate the cause (whether it’s missing documentation, incorrect coding, or authorization issues) and work to appeal when possible. More importantly, they implement process improvements to prevent repeat denials. Hospitals with a strong denial prevention strategy can recover millions in otherwise lost revenue annually.
Step 10 – Patient Billing and Statement Delivery
After insurance payments are posted, the patient is billed for any remaining balance. Patient billing in RCM should be simple, clear, and timely. Offering statements via multiple channels, including email, text, and paper, improves the likelihood of prompt payment. Providing itemized bills and easy-to-understand summaries also reduces billing inquiries and disputes.
Step 11 – Patient Payment Collection
The patient payment collection step focuses on ensuring balances are paid promptly. Hospitals can increase collection rates by offering multiple payment options, such as online portals, IVR payments, mobile payment links, and in-person transactions. Automated payment reminders by SMS, voice, or email are proven to reduce A/R days and improve cash flow. Flexible payment plans can also make it easier for patients to meet their obligations without financial strain.
Step 12 – Collections and A/R Follow-Up
If balances remain unpaid, the collections process in hospital RCM requires strategic follow-up. For patient accounts, this may involve a series of reminder calls, letters, or outsourcing to a collection agency. For insurance accounts, it may require resubmission or payer escalation. Timely A/R follow-up prevents accounts from aging beyond recovery and minimizes write-offs.
Step 13 – Reporting and Performance Analysis
The final step in the healthcare revenue cycle involves reviewing key performance indicators (KPIs) to track efficiency and pinpoint issues. Metrics such as days in A/R, denial rate, net collection rate, and clean claim rate help leaders make informed decisions. Regular reporting also supports compliance and ensures the revenue cycle remains aligned with organizational goals. Hospitals that adopt real-time analytics can respond to trends faster, making continuous improvement a reality.
When viewed as a whole, these 13 steps demonstrate that hospital revenue cycle management is about billing but also building a coordinated, efficient, and patient-friendly process that supports financial sustainability.

Hospital Revenue Cycle Management: Processes & Best Practices
Hospital revenue cycle management (RCM) follows the same foundational principles as general healthcare RCM, but it operates on a larger, more complex scale. Hospitals typically manage higher patient volumes, a wider variety of services, and more extensive billing requirements, making efficiency and accuracy critical.
How Hospital RCM Differs from General Healthcare RCM
While private practices or specialty clinics often focus on a smaller set of procedures and a limited payer mix, hospitals handle everything from emergency care to elective surgeries across multiple departments. This complexity increases the number of claim types, coding variations, and payer-specific requirements. Hospital RCM teams must coordinate across diverse service lines to ensure every charge is captured and billed correctly.
Hospitals also face unique compliance demands. Regulatory requirements such as HIPAA, CMS rules, and state-specific mandates are more extensive in hospital environments, and failure to comply can lead to financial penalties and reputational damage.
Importance for Large Health Systems vs. Small Hospitals
For large health systems, RCM must integrate data from multiple facilities, potentially across different states or regions. Centralized RCM platforms help standardize workflows, enforce compliance, and consolidate reporting. In contrast, smaller hospitals may rely on leaner RCM teams that manage every stage of the cycle in-house. These hospitals benefit from automation tools that reduce manual tasks and allow limited staff to focus on exceptions and problem accounts.
Regardless of size, both large and small hospitals benefit from clearly defined processes, regular training for staff, and consistent monitoring of KPIs such as days in A/R, clean claim rate, and denial rate.
Best Practices for Hospital Revenue Cycle Management
Implementing proven best practices can significantly improve hospital RCM performance:
- Invest in staff training: Regular training on coding updates, payer requirements, and compliance guidelines reduces errors and increases first-pass claim acceptance rates.
- Adopt automation strategically: Tools such as automated eligibility verification, charge capture, and denial management software can streamline high-volume tasks and reduce manual errors.
- Strengthen patient engagement: Offering online portals, payment plans, and upfront cost estimates improves patient satisfaction and increases payment compliance.
- Use data-driven decision-making: Regularly review RCM reports to identify bottlenecks, high-denial areas, or departments with consistent revenue leakage.
- Coordinate across departments: Clinical teams, front office staff, and billing departments should work collaboratively to ensure accurate documentation and timely billing.
Hospitals that consistently apply these practices can reduce A/R days, minimize write-offs, and improve overall financial stability. Whether managing a large multi-hospital system or a smaller regional facility, the right RCM processes help secure timely reimbursements, maintain compliance, and support high-quality patient care.

Key Metrics & KPIs for Hospital & Healthcare RCM
Tracking the right revenue cycle KPIs is essential for evaluating the financial health of hospitals and healthcare organizations. These metrics help identify inefficiencies, measure progress toward goals, and guide process improvements. Without clear benchmarks, it’s difficult to know whether your revenue cycle management strategies are truly effective.
Why KPIs Matter in Hospital Revenue Cycle Management
In hospital environments, the volume of transactions and diversity of services create multiple points where revenue can be lost. KPIs provide a measurable way to monitor performance at each stage of the cycle, from patient registration to final payment posting. Regular KPI tracking enables leaders to pinpoint issues such as delayed claims, high denial rates, or slow patient payments before they significantly impact cash flow.
Core KPIs Every Hospital Should Track
While there are dozens of potential indicators, some KPIs are critical for both hospitals and healthcare systems:
- Days in Accounts Receivable (A/R): The average number of days it takes to collect payments after a service is provided.
- Clean Claim Rate: The percentage of claims accepted and paid without edits or rework.
- Denial Rate: The percentage of claims rejected by payers; a high rate signals documentation or process issues.
- Net Collection Rate: Measures the percentage of collectible revenue actually collected after payer adjustments.
- First Pass Resolution Rate (FPRR): The percentage of claims paid in full after the first submission.
- Bad Debt as a Percentage of Revenue: Tracks the portion of revenue lost to uncollectible patient balances.
- Cost to Collect: The total cost of collecting revenue, including staff time, technology, and vendor fees.
Common Challenges in RCM & How to Solve Them
Even the most well-structured hospital revenue cycle management process faces obstacles that can slow payments, increase costs, and impact patient satisfaction. Recognizing these challenges early, and implementing targeted solutions, is essential for keeping the revenue cycle running efficiently and protecting financial stability.
Billing Errors and Claim Denials
Billing errors remain one of the most common causes of revenue leakage in hospitals. They can occur due to inaccurate medical coding, incomplete patient demographics, incorrect insurance information, or missing clinical documentation. Each error increases the likelihood of claim denials, which require additional time, staff resources, and sometimes external assistance to resolve.
Solution:
- Implement automated claim scrubbing tools to detect and correct common errors before submission.
- Provide ongoing staff training on payer-specific rules, coding updates, and documentation requirements.
- Track denial rate trends by department or payer to identify recurring issues and adjust processes accordingly.

Delayed Payments and High A/R Days
Slow payment cycles can create significant cash flow problems, especially for hospitals managing large patient volumes. Delays often occur because of lengthy payer processing times, incomplete claims, or patients struggling to pay their portion of the bill.
Solution:
- Offer multiple payment channels, including online portals, IVR systems, mobile payment links, and in-person options.
- Use automated payment reminders via SMS, voice, and email to prompt patients before due dates.
- Negotiate electronic remittance advice (ERA) agreements with payers to shorten payment posting times.
Compliance Risks
Hospitals operate within a complex regulatory framework that includes HIPAA, CMS guidelines, and state-specific healthcare laws. Non-compliance can lead to financial penalties, reputational harm, and loss of patient trust.
Solution:
- Select RCM systems that maintain PCI and HIPAA compliance and automatically update to meet new regulations.
- Limit access to sensitive patient payment data through role-based permissions.
- Conduct regular internal audits and mock compliance checks to identify and address potential vulnerabilities.
Staffing Shortages and High Turnover
Revenue cycle management relies on experienced staff for scheduling, coding, billing, and collections. Many hospitals face ongoing staffing shortages or high turnover, which disrupts workflows and increases the risk of errors.
Solution:
- Crosstrain team members so they can cover multiple functions during staffing gaps.
- Automate repetitive and time-consuming tasks, allowing staff to focus on higher-value activities.
- Engage healthcare revenue cycle consultants during periods of rapid growth or backlog accumulation.
Hospital Revenue Cycle Optimization Opportunities
Many hospitals have untapped opportunities to improve efficiency, but they may lack visibility into problem areas. Common improvement areas include reducing manual data entry, improving charge capture, and enhancing denial appeal processes.
Solution:
- Use advanced analytics to pinpoint bottlenecks and track improvements over time.
- Benchmark performance metrics against similar facilities to set realistic goals.
- Review workflows quarterly to ensure alignment with best practices and new technology capabilities.
By proactively addressing these challenges, hospitals can enhance healthcare revenue cycle performance, accelerate collections, reduce costs, and improve patient experiences. Laying this groundwork also prepares organizations to successfully adopt advanced tools and strategies, which will be explored in the next section on technology, AI, and automation.

Technology, AI, and Automation in Revenue Cycle Management
The use of technology in healthcare revenue cycle management is no longer optional. Hospitals and healthcare systems are adopting automation, artificial intelligence (AI), and predictive analytics to improve accuracy, speed up collections, and reduce administrative costs. These tools can streamline workflows across the entire revenue cycle, from patient registration to final payment posting.
Role of AI in Revenue Cycle Management
AI in healthcare revenue cycle management helps organizations process large volumes of data quickly and accurately. AI algorithms can identify coding errors, predict claim denials, and flag high-risk accounts for early intervention. This allows staff to focus on complex cases while routine tasks are handled automatically. AI can also be used to forecast payment timelines, helping finance teams manage cash flow more effectively.
For example, an AI-powered denial management system can analyze historical data to determine the most common reasons for denials and recommend corrective actions before claims are submitted. This not only improves first-pass resolution rates but also reduces the cost of rework.
Predictive Analytics for Better Decision-Making
Predictive analytics uses historical and real-time data to anticipate future outcomes. In RCM, this technology can forecast trends in patient payments, identify potential delays in claims processing, and suggest the best strategies for collections. Hospitals can use predictive insights to optimize staffing levels, prioritize high-value accounts, and reduce days in accounts receivable (A/R).
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) for Efficiency
RPA in healthcare revenue cycle management automates repetitive, rule-based tasks such as data entry, insurance verification, and payment posting. By reducing manual work, RPA helps lower error rates, accelerates transaction times, and frees staff to focus on revenue-generating activities.
For example, an RPA bot can automatically pull patient insurance data from a portal, verify eligibility, and update the hospital’s RCM system without human intervention. This not only saves time but also ensures consistency across records.
Benefits of Technology Integration
Hospitals that invest in technology integration across their RCM processes see measurable results, including:
- Increased clean claim rates and faster payer reimbursements
- Reduced operational costs due to automation of high-volume tasks
- Improved compliance through standardized, trackable workflows
- Enhanced patient experience with self-service portals and digital payment options
By leveraging AI, predictive analytics, and automation, hospitals can transform their revenue cycle into a more efficient, accurate, and patient-friendly process. In the next section, we will explore specific strategies for streamlining patient payments using automation and digital tools, which directly improve cash flow and reduce A/R days.

Hospitals and healthcare providers often struggle with slow patient payments, high days in accounts receivable (A/R), and inefficient billing processes. These challenges can create cash flow issues and increase administrative workloads. By adopting automation in patient payment collection, organizations can simplify payment workflows, reduce manual effort, and offer patients more convenient ways to pay.
Automated payment solutions not only accelerate collections but also enhance the patient experience by making transactions secure, transparent, and available 24/7.
Automated Payment Reminders for Faster Collections
Automated payment reminders are one of the most effective ways to reduce overdue balances and improve collection rates. These reminders can be sent through multiple channels, including voice calls, SMS text messages, and email.
Unlike manual follow-up, automated reminders are consistent, timely, and scalable, allowing hospitals to reach hundreds or thousands of patients without increasing staff workload. Messages can be personalized with patient names, due dates, and balance amounts, making them more relevant and actionable.
Using a voice-based IVR system, for example, patients can be reminded of an upcoming payment and be given the option to pay immediately over the phone. Similarly, an SMS reminder can include a secure payment link that takes the patient directly to an online portal. This approach shortens the payment cycle and reduces the number of accounts sent to collections.
Web Pay Links and Self-Service Portals
Self-service payment portals and secure web pay links give patients the ability to pay at their convenience, without waiting for office hours or staff availability. Hospitals can integrate these tools with their revenue cycle management systems to ensure that payments are posted in real time.
Web pay links can be sent via text, email, or included in electronic statements. These links take patients to a secure checkout page where they can review their balance, choose a payment method, and receive an immediate confirmation.
Self-service portals often go beyond payments, allowing patients to view statements, set up recurring payments, and manage their billing preferences. This level of control increases patient satisfaction and reduces inbound billing inquiries.
IVR Payments and Advanced Payment Options
IVR Payments is an advanced, secure payment platform that enables patients to make payments through an automated phone system without speaking to a live representative. This reduces call center workload, improves payment security, and ensures compliance with PCI standards.
IVR Payments supports multiple payment methods, including credit and debit cards, electronic checks, and in some cases, digital wallet or cryptocurrency payments. By diversifying payment options, hospitals can accommodate a wider range of patient preferences and improve overall collection rates.
For example, a patient who receives a reminder call through CryptoIVR can complete their payment immediately, without being transferred or placed on hold. This seamless experience increases the likelihood of prompt payment and reduces administrative overhead.
Want to reduce A/R days and improve cash flow without increasing staff workload? Automated payment reminders, self-service portals, and advanced IVR solutions like CryptoIVR can integrate directly with your hospital’s revenue cycle, making it easier for patients to pay and faster for you to collect.
Outsourcing & Consulting for Hospital Revenue Cycle
For some hospitals, managing the entire revenue cycle in-house can be challenging, especially when faced with staffing shortages, rapid growth, or complex billing requirements. In these cases, outsourcing certain RCM functions or partnering with healthcare revenue cycle consultants can help maintain efficiency, accuracy, and compliance.
When to Consider Outsourcing
Hospitals often consider outsourcing when:
- Claim backlogs are growing faster than internal staff can manage.
- Denial rates are consistently above industry benchmarks.
- Technology limitations make automation and integration difficult.
- Specialized expertise is required for areas such as coding audits or compliance reviews.
By delegating certain tasks (such as coding, claim follow-up, or patient payment collection) hospitals can free up internal staff to focus on patient-facing and high-value activities. Outsourcing partners often have advanced technology and specialized teams that can accelerate collections and improve cash flow.
Role of Healthcare Revenue Cycle Consultants
Consultants bring deep industry knowledge and experience in optimizing hospital RCM processes. They can assess current workflows, identify inefficiencies, and recommend solutions tailored to the organization’s size, market, and payer mix. Consultants may also help with:
- Implementing automation and AI tools.
- Training staff on best practices and compliance requirements.
- Redesigning workflows to improve clean claim rates and reduce days in A/R.
Whether through a short-term engagement to resolve specific challenges or a long-term partnership to manage ongoing operations, consultants can provide the expertise and external perspective needed to keep hospital revenue cycles performing at a high level.
Outsourcing and consulting are not one-size-fits-all solutions, but when applied strategically, they can help hospitals stabilize cash flow, reduce errors, and improve both patient and payer relationships.
Regional & Market Insights
The healthcare revenue cycle management market varies significantly by region, shaped by differences in regulations, payer structures, and technology adoption rates. Understanding these differences is important for hospitals and healthcare systems seeking to improve their RCM processes or expand into new markets.
United States
In the U.S., the revenue cycle is heavily influenced by a complex mix of private insurance, Medicare, and Medicaid. Hospitals face significant administrative burdens related to prior authorizations, coding updates, and payer-specific rules. Adoption of automation, AI, and patient self-service tools is growing quickly, driven by the need to reduce costs and improve patient satisfaction.
Canada
Revenue cycle management in Canadian healthcare operates within a publicly funded system, but hospitals still manage private pay, supplemental insurance, and non-covered services. Efficiency gains often come from improving internal workflows and reducing billing errors, particularly for services billed outside provincial health coverage.
GCC (Gulf Cooperation Council)
The GCC healthcare revenue cycle management market is expanding rapidly due to growing private healthcare investment and the introduction of mandatory health insurance in several countries. Hospitals are increasingly adopting international best practices, including automation and outsourcing, to handle higher patient volumes and diverse payer requirements.
India
In India, the healthcare sector is experiencing strong growth, with a mix of public and private providers. Many private hospitals are modernizing their revenue cycle processes to accommodate increased patient demand and medical tourism. Opportunities exist for implementing automated billing, electronic claims submission, and digital payment platforms to reduce inefficiencies.
Understanding regional differences allows healthcare providers to adopt the most effective RCM strategies for their market, whether that means prioritizing compliance, streamlining private pay billing, or scaling operations to meet rapid growth.
Conferences & Industry Resources
Staying informed about the latest trends, regulations, and technologies in hospital revenue cycle management is essential for maintaining competitive performance. Industry conferences and resources provide valuable opportunities for networking, learning, and discovering new solutions.
Key Conferences
One of the most recognized events in this space is the Becker’s Hospital Review Revenue Cycle Conference, which gathers healthcare leaders, RCM executives, and technology providers to discuss strategies for improving financial outcomes. Sessions often cover topics such as denial management, automation, patient financial engagement, and compliance best practices.
Other notable events include the HFMA Annual Conference and regional health finance forums, which provide targeted insights for specific markets or facility types.
Industry Resources
Keeping up with revenue cycle management healthcare news through reputable publications like Becker’s Hospital Review, HFMA, and Modern Healthcare ensures hospital leaders remain aware of industry changes. Webinars, whitepapers, and vendor case studies can also offer actionable strategies for process improvement.
By actively engaging with industry events and trusted resources, hospitals can stay ahead of emerging challenges, adopt proven best practices, and make informed decisions that strengthen their revenue cycle performance.
Optimize Your Revenue Cycle
A healthy revenue cycle is the foundation of financial stability for any hospital or healthcare organization. By streamlining processes, adopting automation, and tracking the right KPIs, you can reduce days in accounts receivable, improve cash flow, and enhance the patient experience.
If your organization is ready to improve collections, reduce billing errors, and implement modern payment solutions, our team can help. We specialize in designing revenue cycle workflows that integrate with your existing systems while maximizing efficiency and compliance.
Whether you need support with denial management, payment automation, or full-cycle RCM consulting, we offer solutions tailored to your facility’s needs and goals.
Contact us today to schedule a consultation and learn how we can help you optimize your hospital’s revenue cycle, improve operational performance, and build a stronger financial future.
FAQ: Hospital vs Healthcare RCM
What is the revenue cycle in a hospital?
The revenue cycle in a hospital is the complete financial process that tracks a patient’s journey from initial registration through final payment. This includes scheduling, insurance verification, coding, claims submission, payment posting, and collections. Hospital revenue cycles are often more complex than those in smaller healthcare settings due to higher patient volumes, multiple service lines, and more extensive compliance requirements.
How is hospital RCM different from healthcare RCM?
Hospital revenue cycle management differs from general healthcare RCM in scale, complexity, and regulatory oversight. While a physician’s office or specialty clinic may manage a limited range of services and payers, hospitals handle emergency care, inpatient and outpatient services, surgical procedures, and diagnostics, often under one system. Hospital RCM must coordinate data and workflows across numerous departments, each with its own documentation and billing requirements.
How can AI improve revenue cycle efficiency?
AI can improve revenue cycle efficiency by automating time-consuming tasks such as claims scrubbing, denial prediction, and payment posting. In hospitals, AI tools can analyze large datasets to identify patterns in payer behaviors, forecast payment delays, and recommend process improvements. This allows staff to focus on complex cases, reduces days in accounts receivable (A/R), and increases clean claim rates.
Hospitals that implement AI within their RCM systems often see faster reimbursements, lower operational costs, and better compliance with payer and regulatory requirements. By combining AI with predictive analytics and robotic process automation, hospitals can create a more efficient, accurate, and patient-friendly revenue cycle.
Additional Resources:
Transitioning from Live Staff Phone Payments to IVR Payments
Accepting Credit Cards Over the Phone to Virtual Terminals PCI compliance
The Uniqueness of CryptoIVR A Proprietary Secure IVR Payment Solution
Introduction to Exchanging Information with Your Business System


